Weight Loss Treatments: Complete Guide to Medical Options (Pills to Surgery)
Embarking on a weight loss journey can feel like navigating a maze blindfolded. You're bombarded with information, quick-fix solutions, and conflicting advice, leaving you wondering which path, if any, truly leads to sustainable results.
The struggle to shed those extra pounds can be incredibly frustrating. Diet fads come and go, exercise routines become monotonous, and the scale stubbornly refuses to budge. The emotional toll of this can be heavy, impacting self-esteem and overall well-being.
This comprehensive guide is designed to illuminate the landscape of medical weight loss options, from prescription pills to surgical interventions. We aim to provide you with a clear understanding of each treatment, its benefits, risks, and suitability, empowering you to make informed decisions in consultation with your healthcare provider.
This article dives deep into the world of medical weight loss, exploring various treatments like prescription medications (such as GLP-1 receptor agonists), minimally invasive procedures (like gastric balloons), and surgical options (such as gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy). We'll cover the science behind each approach, potential side effects, lifestyle changes required, and factors to consider when choosing the right option for you. Get ready to explore medical weight loss, weight loss pills, weight loss surgery, bariatric surgery, gastric bypass, and lifestyle modifications all in one place.
My Personal Weight Loss Journey and the Role of Medical Options
For years, I battled with my weight. It wasn't just about fitting into smaller clothes; it was about my health, my energy levels, and my overall quality of life. I tried countless diets, from the trendy ones that promised rapid results to more sustainable approaches focused on whole foods. I even became a gym rat for a while, pushing myself through grueling workouts. While I saw some initial success, I always seemed to plateau or, even worse, regain the weight I'd lost. The constant cycle of hope and disappointment was incredibly disheartening.
It wasn't until I spoke with my doctor that I truly understood the role medical interventions could play. He explained that for some individuals, particularly those with underlying health conditions or a significant amount of weight to lose, medical options could be a valuable tool, especially when combined with lifestyle changes. We discussed various prescription medications, their mechanisms of action, and the potential side effects. While I ultimately decided to focus on lifestyle modifications with the support of a registered dietitian, the conversation opened my eyes to the possibilities that medical weight loss offers. It also highlighted the importance of having an honest discussion with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action. Weight loss isn't one-size-fits-all. What works for one person may not work for another. Medical options, like weight loss pills, can be effective for some, but they always come with risks and require careful monitoring. Similarly, weight loss surgery, such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, can be life-changing for individuals with severe obesity, but it's a major decision that requires thorough evaluation and commitment to long-term lifestyle changes. Remember, medical options are most effective when combined with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and behavioral therapy. They're not a magic bullet, but rather a powerful tool to support your weight loss journey.
Understanding Weight Loss Medications
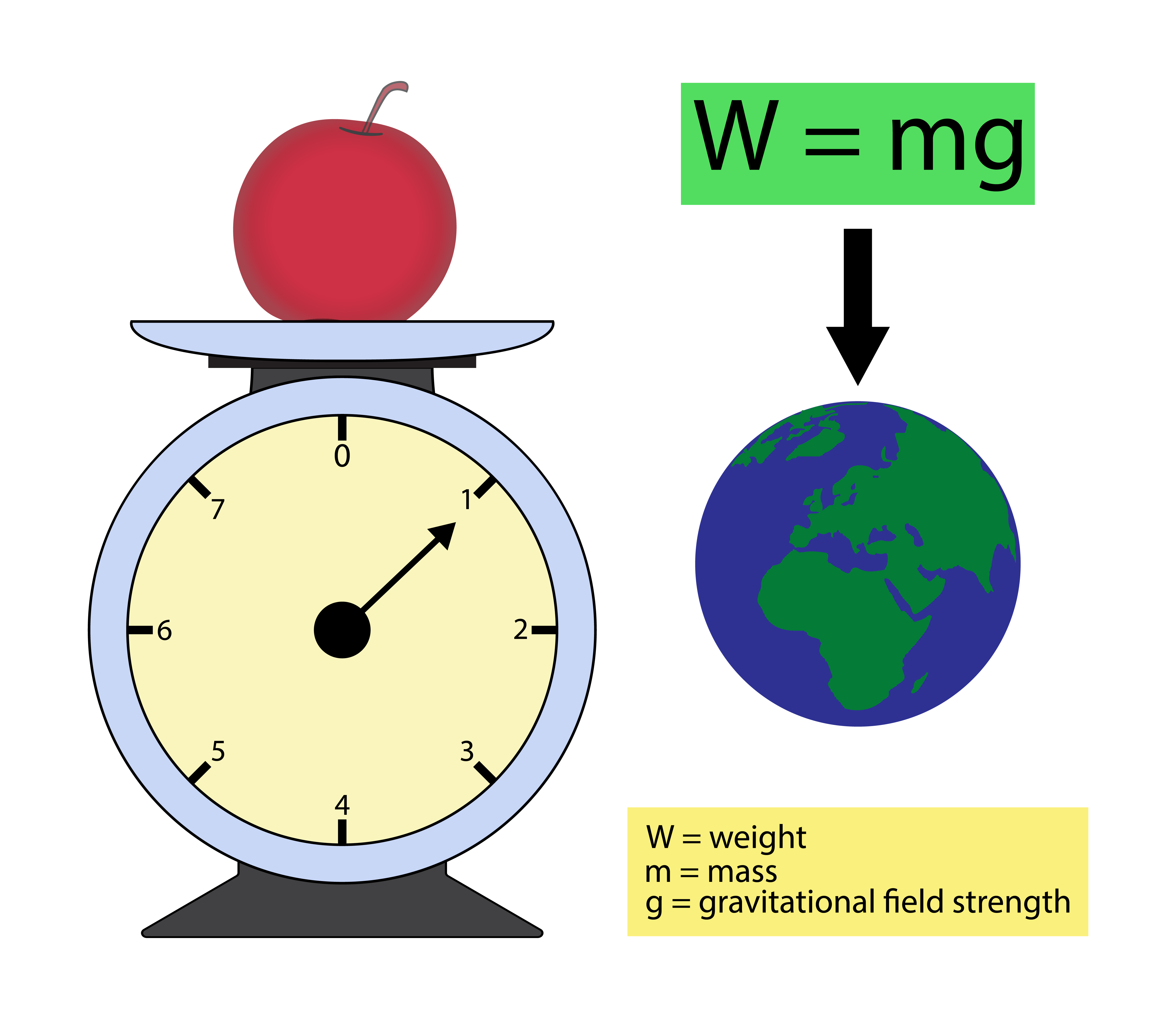
Weight loss medications, also known as anti-obesity drugs, are prescription medications designed to help individuals lose weight by reducing appetite, increasing feelings of fullness, or interfering with the absorption of fat. These medications are typically prescribed for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher, or a BMI of 27 or higher with weight-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol.
Several different types of weight loss medications are available, each working through different mechanisms. Some, like phentermine, are appetite suppressants that stimulate the central nervous system, reducing hunger cravings. Others, like orlistat, work by blocking the absorption of dietary fat in the intestines. More recently, GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as semaglutide and liraglutide, have gained popularity for their effectiveness in promoting weight loss by regulating blood sugar levels, slowing down gastric emptying, and increasing feelings of fullness. It's important to note that weight loss medications are not a standalone solution. They are most effective when used in conjunction with a healthy diet and regular exercise. The ideal candidate for weight loss medication is someone who has struggled to lose weight through diet and exercise alone, and who is committed to making long-term lifestyle changes. Potential side effects vary depending on the specific medication. Common side effects may include nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. More serious side effects are possible, so it's crucial to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor. Before starting any weight loss medication, it's essential to have a thorough medical evaluation to determine if it's safe and appropriate for you. Your doctor will consider your medical history, current medications, and any underlying health conditions. Remember, weight loss medications are a tool to support your weight loss journey, but they require a holistic approach that includes healthy habits and ongoing medical supervision.
The History and Myths of Weight Loss Treatments
The quest for weight loss is as old as time itself, with historical records revealing various (and often bizarre) methods used throughout the centuries. From ancient Egyptians consuming laxatives to Victorian-era tapeworm diets, the desperation for a quick fix has always been present. In the early 20th century, amphetamines were marketed as weight loss pills, leading to widespread abuse and severe health consequences. This history highlights the importance of scientific evidence and safety regulations in the development and use of weight loss treatments.
One persistent myth is that weight loss is simply a matter of willpower. This belief ignores the complex interplay of genetics, hormones, metabolism, and environmental factors that contribute to weight gain and obesity. While willpower plays a role, it's not the sole determinant of success. Another myth is that all weight loss pills are dangerous. While some weight loss supplements have been found to be harmful or ineffective, FDA-approved prescription medications undergo rigorous testing to ensure their safety and efficacy. However, it's crucial to remember that all medications have potential side effects, and it's essential to discuss these with your doctor. The rise of fad diets and weight loss scams further contributes to the misinformation surrounding weight loss. Promises of rapid weight loss without any effort are often too good to be true and can even be harmful. Sustainable weight loss requires a holistic approach that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and behavioral changes. Medical interventions, such as weight loss medications and bariatric surgery, can be valuable tools, but they are most effective when combined with lifestyle modifications. Understanding the history and myths surrounding weight loss treatments empowers individuals to make informed decisions based on scientific evidence rather than misleading claims.
Unveiling the Hidden Secrets of Sustainable Weight Loss
The "hidden secret" of sustainable weight loss isn't really a secret at all. It's about embracing a holistic approach that addresses the root causes of weight gain and fosters long-term lifestyle changes. It's not about quick fixes or restrictive diets, but rather about creating a healthy relationship with food, incorporating regular physical activity, and managing stress effectively.
One often overlooked aspect is the importance of behavioral therapy. Addressing emotional eating, identifying triggers, and developing coping mechanisms are crucial for long-term success. Working with a therapist or counselor can provide valuable support and guidance in navigating the emotional challenges of weight loss. Another key element is building a strong support system. Surrounding yourself with supportive friends, family members, or a weight loss group can provide encouragement and accountability. Sharing your struggles and successes with others who understand can make the journey feel less isolating. The role of sleep in weight management is also often underestimated. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite, leading to increased cravings and weight gain. Aiming for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night can have a significant impact on your weight loss efforts. Finally, it's important to be patient and kind to yourself. Weight loss is a journey, not a destination. There will be setbacks and challenges along the way. Instead of getting discouraged, learn from your mistakes and focus on making progress, not perfection. Sustainable weight loss is about creating a lifestyle that supports your health and well-being. It's about finding a balance that works for you and making gradual changes that you can maintain over the long term. Remember, it's not about deprivation, but rather about nourishing your body with healthy foods and engaging in activities that you enjoy.
Recommendations for Choosing the Right Weight Loss Treatment
Choosing the right weight loss treatment is a personal decision that should be made in consultation with your healthcare provider. There's no one-size-fits-all approach, and the best option for you will depend on your individual health status, weight loss goals, and preferences. Start by having an honest conversation with your doctor about your weight and your concerns. They can assess your overall health, evaluate any underlying medical conditions, and discuss the potential benefits and risks of different treatment options.
Consider your BMI and any weight-related health conditions. If you have a BMI of 30 or higher, or a BMI of 27 or higher with weight-related health conditions, you may be a candidate for weight loss medications or bariatric surgery. If your BMI is lower, lifestyle modifications may be the most appropriate approach. Research different treatment options and understand how they work. Learn about the potential side effects, long-term outcomes, and lifestyle changes required. Don't rely solely on information from the internet; seek reliable sources such as your doctor, registered dietitian, or reputable medical websites. Set realistic goals and expectations. Weight loss is a gradual process, and it's important to have realistic expectations about how quickly you can lose weight and how much weight you can expect to lose. Focus on making sustainable changes that you can maintain over the long term. Consider the cost and insurance coverage of different treatments. Weight loss medications and bariatric surgery can be expensive, and insurance coverage may vary. Check with your insurance provider to understand your coverage and any out-of-pocket costs. Finally, be prepared to commit to long-term lifestyle changes. Medical interventions are most effective when combined with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and behavioral therapy. If you're not willing to make these changes, you're less likely to achieve long-term success. Choosing the right weight loss treatment is a collaborative process. Work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that meets your individual needs and goals.
The Role of Lifestyle Modifications in Medical Weight Loss
Lifestyle modifications are the cornerstone of any successful weight loss program, whether or not medical interventions are involved. These modifications encompass changes to your diet, exercise habits, and overall behavior, and they play a crucial role in achieving and maintaining weight loss over the long term. A healthy diet is essential for weight loss. Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Limit your intake of sugary drinks, processed foods, and unhealthy fats. Work with a registered dietitian to develop a meal plan that meets your individual needs and preferences. Regular physical activity is also crucial for weight loss. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking, jogging, or swimming. In addition, incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week to build muscle mass and boost your metabolism. Behavioral therapy can help you identify and address the emotional and psychological factors that contribute to weight gain. This may involve learning strategies for managing stress, coping with cravings, and developing healthy eating habits. Lifestyle modifications are not just about losing weight; they're about improving your overall health and well-being. Making these changes can reduce your risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and some types of cancer. Even small changes to your lifestyle can have a big impact on your health. Start by making one or two small changes at a time, such as adding a serving of vegetables to each meal or walking for 30 minutes a day. As you become more comfortable with these changes, you can gradually add more. Remember, lifestyle modifications are a long-term commitment. It's important to find changes that you can maintain over the long term and to be patient and kind to yourself along the way. There will be setbacks and challenges along the way. Instead of getting discouraged, learn from your mistakes and focus on making progress, not perfection.
Tips for Maximizing the Effectiveness of Weight Loss Treatments
To truly maximize the effectiveness of any weight loss treatment, be it medication, surgery, or lifestyle changes, it's crucial to approach it with a holistic mindset and a commitment to long-term health. Consistency is key. Whether you're taking medication, following a diet plan, or engaging in regular exercise, consistency is essential for achieving and maintaining results. Stick to your plan as closely as possible, even when you're feeling tempted to stray. Track your progress. Monitoring your weight, measurements, and food intake can help you stay motivated and identify areas where you need to make adjustments. Use a journal, app, or spreadsheet to track your progress and celebrate your successes. Stay hydrated. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help you feel full, boost your metabolism, and flush out toxins. Aim for at least eight glasses of water per day. Get enough sleep. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite, leading to increased cravings and weight gain. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night. Manage stress. Stress can trigger emotional eating and lead to weight gain. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time in nature. Seek support. Surround yourself with supportive friends, family members, or a weight loss group. Sharing your struggles and successes with others who understand can make the journey feel less isolating. Be patient. Weight loss takes time and effort. Don't get discouraged if you don't see results immediately. Focus on making sustainable changes that you can maintain over the long term. Celebrate your successes. Acknowledge and celebrate your achievements along the way, no matter how small. This will help you stay motivated and build confidence. Don't be afraid to ask for help. If you're struggling to lose weight or manage your weight loss treatment, don't hesitate to reach out to your doctor, registered dietitian, or therapist for support and guidance.
Understanding the Different Types of Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery, also known as weight loss surgery, encompasses a range of surgical procedures designed to help individuals with severe obesity lose weight. These procedures work by altering the digestive system to limit the amount of food that can be consumed or absorbed, or both. There are several different types of bariatric surgery, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Gastric bypass is one of the most common types of bariatric surgery. It involves creating a small pouch in the stomach and connecting it directly to the small intestine, bypassing a large portion of the stomach and duodenum. This reduces the amount of food that can be consumed and absorbed, leading to weight loss. Sleeve gastrectomy involves removing a large portion of the stomach, creating a smaller, tube-shaped stomach. This reduces the amount of food that can be consumed and also reduces the production of ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates appetite. Adjustable gastric banding involves placing a band around the upper part of the stomach, creating a smaller pouch. The band can be adjusted to control the size of the opening between the pouch and the rest of the stomach, limiting the amount of food that can be consumed. Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch is a more complex type of bariatric surgery that involves removing a large portion of the stomach and bypassing a significant portion of the small intestine. This reduces the amount of food that can be consumed and absorbed, leading to significant weight loss. The choice of which type of bariatric surgery is best for you will depend on your individual health status, weight loss goals, and preferences. Your surgeon will discuss the different options with you and help you make an informed decision.
Fun Facts About Weight Loss and Metabolism
Did you know that muscle burns more calories than fat, even when you're at rest? That's why strength training is so important for boosting your metabolism and losing weight! Or that spicy foods can actually help you burn more calories? Capsaicin, the compound that gives chili peppers their heat, has been shown to increase metabolism and suppress appetite. It's fascinating how our bodies work, isn't it?
Another fun fact: your metabolism slows down as you age. This is due in part to a decrease in muscle mass and hormonal changes. However, you can counteract this slowdown by staying active and maintaining a healthy diet. Studies have shown that people who eat breakfast tend to weigh less than those who skip it. This is because breakfast helps to kickstart your metabolism and regulate your appetite throughout the day. And speaking of appetite, did you know that stress can actually increase your cravings for unhealthy foods? When you're stressed, your body releases cortisol, a hormone that can trigger cravings for sugary and fatty foods. Getting enough sleep is also crucial for weight management. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite, leading to increased cravings and weight gain. Finally, did you know that laughter can actually burn calories? A good belly laugh can increase your heart rate and burn a small amount of calories. So go ahead and indulge in some humor – it's good for your health! Understanding the science behind weight loss and metabolism can empower you to make informed decisions about your health and well-being. It's not just about counting calories; it's about nourishing your body with healthy foods, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress effectively.
How to Prepare for Weight Loss Treatment
Preparing for weight loss treatment, whether it involves medication, surgery, or intensive lifestyle changes, is crucial for maximizing your chances of success and minimizing potential complications. It's not just about the physical aspects; it's also about the mental and emotional preparation required to embark on this journey.
First and foremost, have an open and honest discussion with your doctor. Discuss your weight loss goals, your medical history, and any concerns you may have. They can assess your overall health, evaluate any underlying medical conditions, and determine if weight loss treatment is right for you. If medication is recommended, understand how it works, the potential side effects, and how to take it properly. Ask your doctor any questions you have and make sure you feel comfortable with the treatment plan. If surgery is being considered, learn about the different types of bariatric surgery, the risks and benefits of each procedure, and the long-term lifestyle changes required. Attend support groups or educational seminars to learn more about the surgery and connect with others who have undergone the procedure. In either case, start making lifestyle changes before you begin treatment. This includes adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress effectively. These changes will help you prepare your body and mind for the demands of weight loss treatment. It's also important to address any emotional issues that may be contributing to your weight gain. This may involve working with a therapist or counselor to address emotional eating, body image issues, or other underlying issues. Finally, build a strong support system. Surround yourself with supportive friends, family members, or a weight loss group. Sharing your struggles and successes with others who understand can make the journey feel less isolating. Preparing for weight loss treatment is a proactive process that involves taking steps to ensure your physical, mental, and emotional readiness. By doing so, you can increase your chances of achieving long-term success and improving your overall health and well-being.
What If Weight Loss Treatments Don't Work?
It's important to acknowledge the possibility that, despite your best efforts, weight loss treatments may not always deliver the desired results. Weight loss is a complex process influenced by various factors, and sometimes, even with medical intervention and lifestyle changes, the scale might not budge as much as you'd hoped. What do you do then?
First, it's crucial to have realistic expectations. Weight loss is not always linear, and plateaus are common. Don't get discouraged if you don't see results immediately. Focus on making sustainable changes that you can maintain over the long term. Re-evaluate your treatment plan. Talk to your doctor about whether the current treatment is still appropriate for you. They may recommend adjusting the dosage of your medication, switching to a different medication, or exploring alternative treatment options. Consider underlying medical conditions. Sometimes, underlying medical conditions can make it difficult to lose weight. Talk to your doctor about any potential medical conditions that may be contributing to your weight gain. Focus on overall health, not just the numbers on the scale. Even if you're not losing weight, you may still be improving your health through lifestyle changes. Focus on eating a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress effectively. Seek support. Surround yourself with supportive friends, family members, or a weight loss group. Sharing your struggles and successes with others who understand can make the journey feel less isolating. Don't give up. Even if weight loss treatments don't work as well as you'd hoped, don't give up on your health goals. Continue to focus on making healthy choices and prioritize your overall well-being. Remember, weight loss is a journey, not a destination. It's important to be patient and kind to yourself along the way. Even if you don't reach your ideal weight, you can still improve your health and quality of life by making positive changes to your lifestyle.
A Listicle of Weight Loss Treatment Options
Navigating the world of weight loss treatments can be overwhelming. To simplify things, here's a listicle summarizing the main options:
1. Lifestyle Modifications: The foundation of any weight loss plan. This includes adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress.
- Over-the-Counter Diet Pills: While widely available, their effectiveness and safety are often questionable. Consult your doctor before trying any of these.
- Prescription Weight Loss Medications: These medications can help suppress appetite, block fat absorption, or regulate blood sugar levels. Examples include phentermine, orlistat, and GLP-1 receptor agonists.
- Endoscopic Procedures: Minimally invasive procedures like gastric balloons can help reduce stomach capacity and promote feelings of fullness.
- Bariatric Surgery: Surgical options like gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding can significantly reduce stomach size and alter the digestive process.
- Behavioral Therapy: Addressing emotional eating, identifying triggers, and developing coping mechanisms are crucial for long-term success.
- Combination Therapy: Combining multiple approaches, such as medication and lifestyle changes, can often lead to better results.
- Emerging Therapies: New weight loss treatments are constantly being developed, including novel medications and minimally invasive procedures. Stay informed about the latest advancements in the field.
- Personalized Nutrition: Tailoring your diet to your individual needs and preferences can make it easier to stick to your weight loss plan.
- Mindful Eating: Paying attention to your hunger cues and eating slowly and deliberately can help you consume fewer calories. This list provides a starting point for exploring the various weight loss treatment options available. Remember to consult with your doctor to determine the best approach for your individual needs and goals.
Question and Answer Section
Here are some frequently asked questions about weight loss treatments:
Q: Are weight loss pills safe?
A: The safety of weight loss pills varies depending on the specific medication and your individual health status. FDA-approved prescription medications undergo rigorous testing to ensure their safety, but all medications have potential side effects. Over-the-counter diet pills are often less regulated and may contain harmful ingredients. Always consult with your doctor before taking any weight loss pills.
Q: How effective is bariatric surgery?
A: Bariatric surgery can be very effective for individuals with severe obesity. Studies have shown that it can lead to significant weight loss and improvements in weight-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea. However, it's important to remember that bariatric surgery is a major procedure that requires long-term lifestyle changes.
Q: What are the risks of weight loss surgery?
A: Like any surgery, bariatric surgery carries certain risks. These may include infection, bleeding, blood clots, and complications related to anesthesia. Long-term risks may include nutritional deficiencies, dumping syndrome, and gallstones. It's important to discuss the risks and benefits of bariatric surgery with your surgeon before making a decision.
Q: Can I lose weight without medical intervention?
A: Yes, many people are able to lose weight through lifestyle modifications alone. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and behavioral therapy can be effective for weight loss. However, for some individuals, medical interventions may be necessary to achieve significant and sustainable weight loss.
Conclusion of Weight Loss Treatments: Complete Guide to Medical Options
Weight loss is a deeply personal journey, and the path to success is rarely a straight line. Understanding the range of medical weight loss options, from pills to surgery, is a crucial first step in making informed decisions about your health. Remember that these treatments are most effective when combined with sustained lifestyle changes. By working closely with your healthcare provider, setting realistic goals, and embracing a holistic approach, you can increase your chances of achieving long-term weight management and improved well-being. The journey may be challenging, but the rewards of a healthier, happier you are well worth the effort.


Post a Comment